How to Choose the Right RF Coaxial Adapter?
 2025.11.12
2025.11.12
 Industry News
Industry News
Choosing the right RF coaxial adapter is crucial, as it's a potential signal bottleneck; an inappropriate choice can directly impact the performance of the entire RF system. Below is an RF coaxial adapter selection guide to help you make the right choice.
1. Key Electrical Parameters (Performance Foundation)
These parameters directly determine whether the adapter can support your operating frequency and power.
Operating Frequency:
This is the primary consideration! It's essential to ensure that the RF coaxial adapter's specified frequency range covers the highest operating frequency of your system.
Different types of RF coaxial adapters have their inherent frequency limits. For example, N-type typically goes up to 11GHz, SMA to 18GHz/26.5GHz, 3.5mm to 33GHz, 2.92mm (K-type) to 40GHz, and 2.4mm to 50GHz.
Principle: The selected adapter's frequency limit should be higher than the highest operating frequency of your system.
Impedance:
The vast majority of RF systems are 50 ohms. Some TV and broadcast equipment may encounter 75-ohm systems.
Make sure it's matched! Never use a 50-ohm adapter in a 75-ohm system, or vice versa, as this will cause severe impedance mismatch and signal reflection.
Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR): A core indicator of matching quality. A VSWR closer to 1:1 is better, indicating less reflection and higher transmission efficiency.
The adapter's VSWR deteriorates with increasing frequency. Consult the product manual to ensure its VSWR meets requirements within your operating frequency band (e.g., < 1.25 in the DC-18GHz range).
Insertion Loss: Power loss as the signal passes through the adapter. A lower value is better, especially in high-frequency and high-power applications.
Losses primarily originate from the conductor and dielectric materials; losses typically increase with higher frequencies.
Rated Power: The maximum average and peak power the adapter can safely handle.
Average power is related to thermal effects; consider the adapter's potential overheating.
Peak power is related to dielectric breakdown and is particularly important in high-power pulse systems.
Always allow for margins! Do not use it at its maximum power.
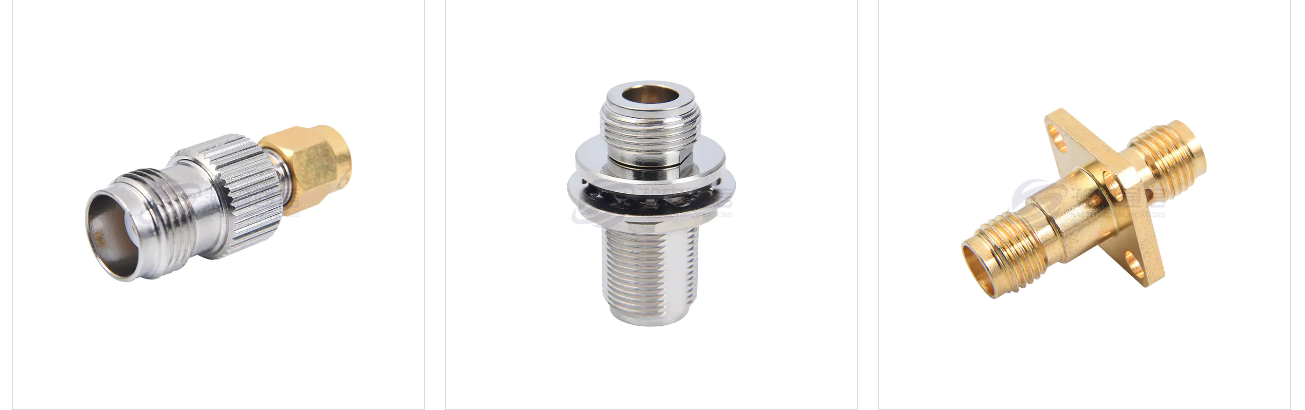

2. Mechanical and Interface Characteristics (Physical Connection)
This is crucial for the correct and reliable installation of the RF coaxial adapter into your system.
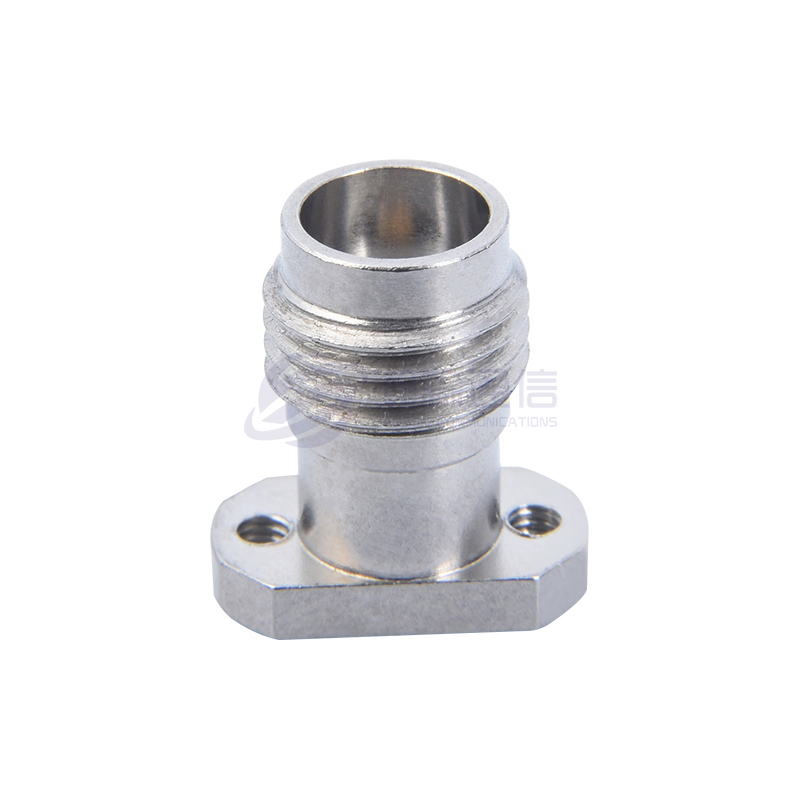
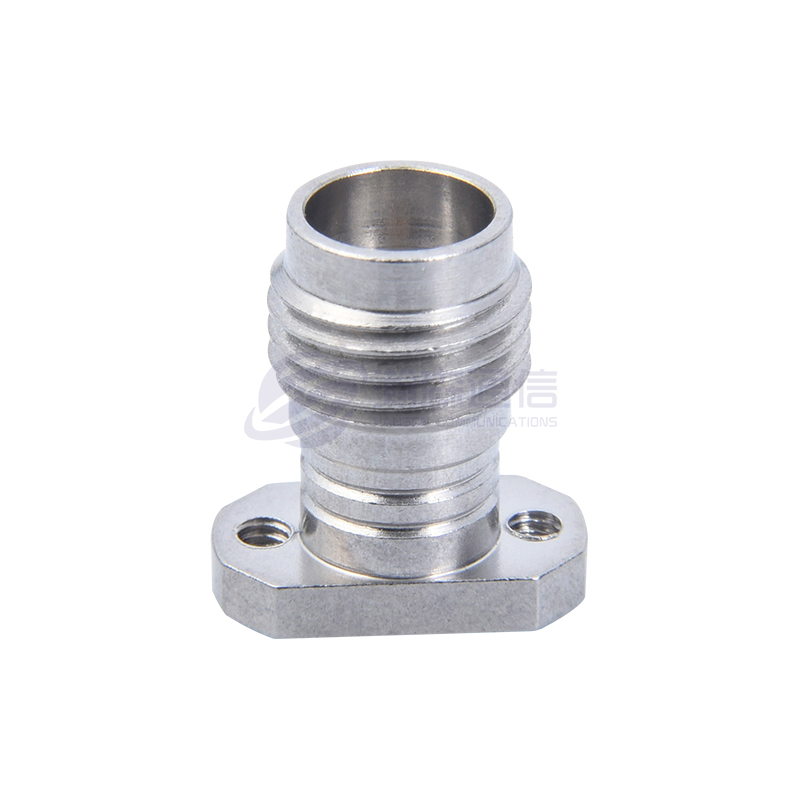
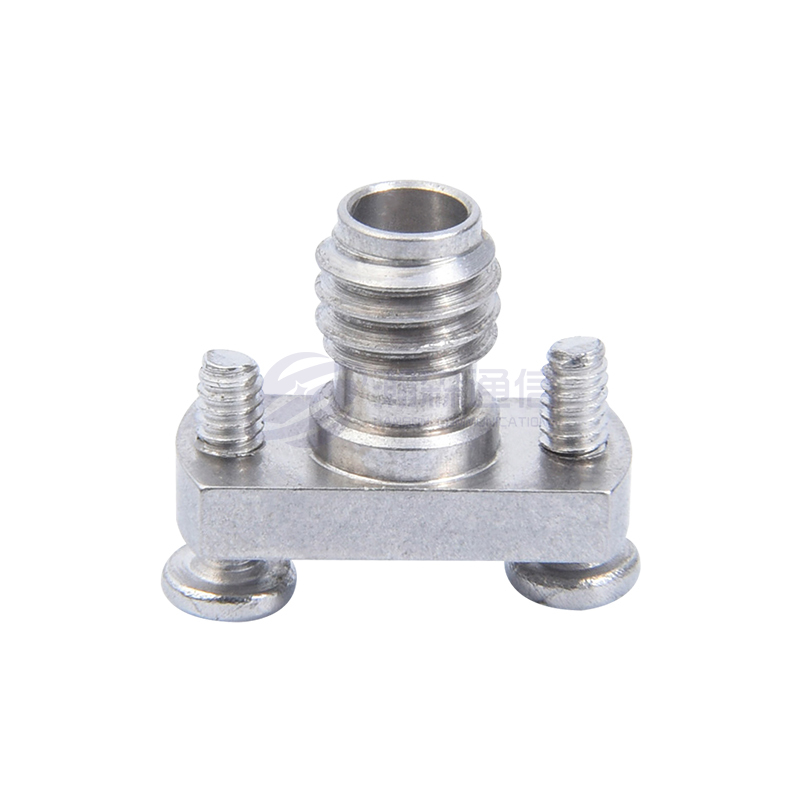
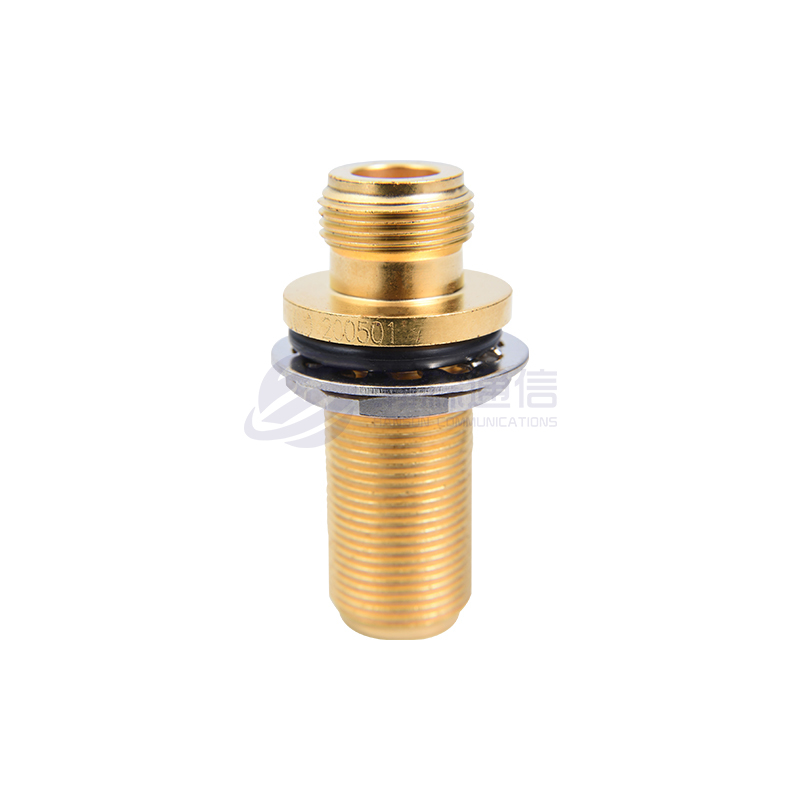
Interface Type and Polarity:
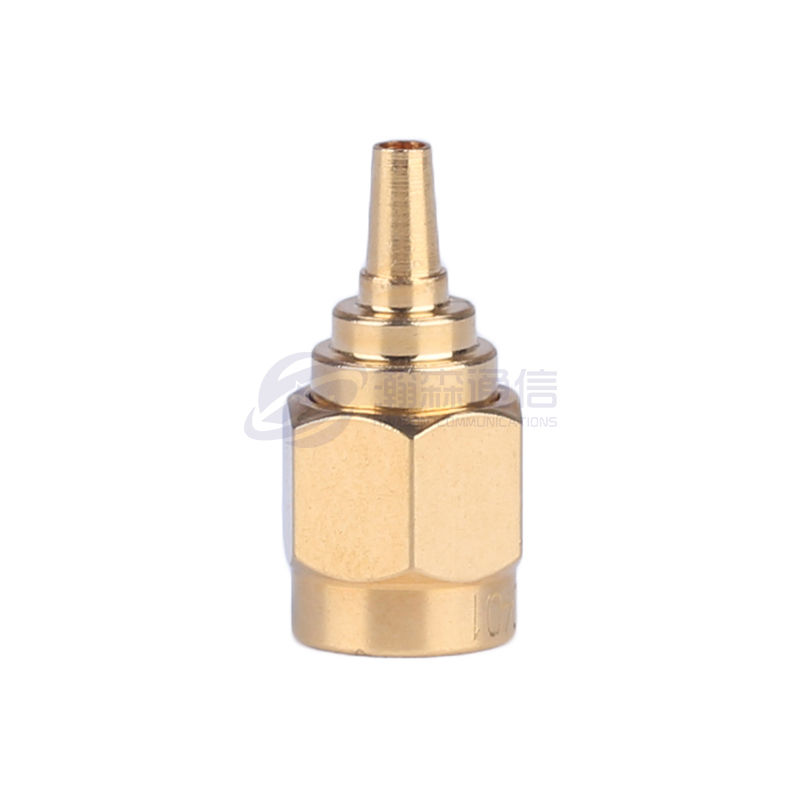
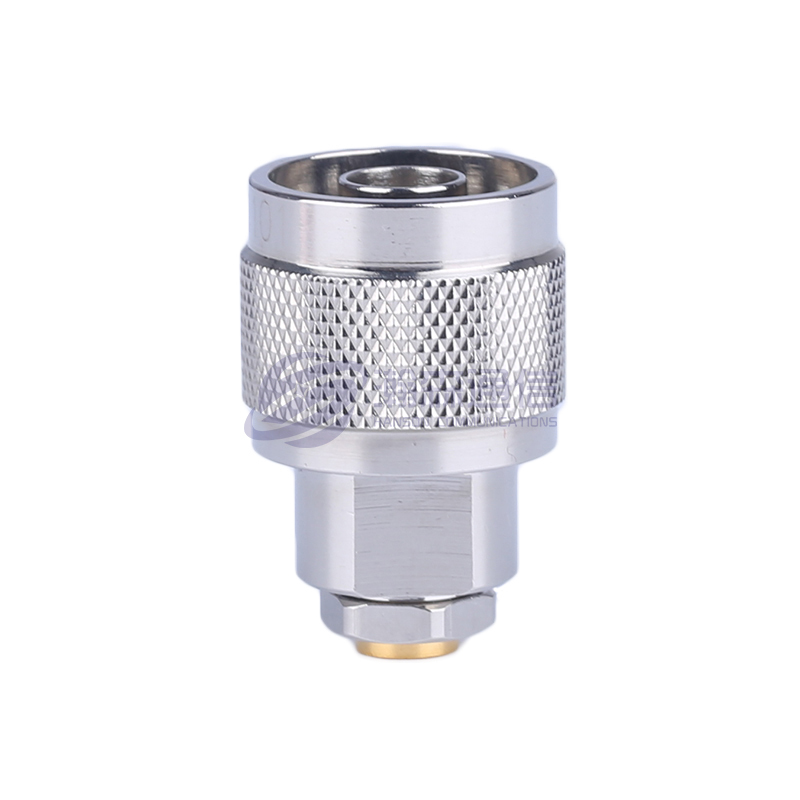
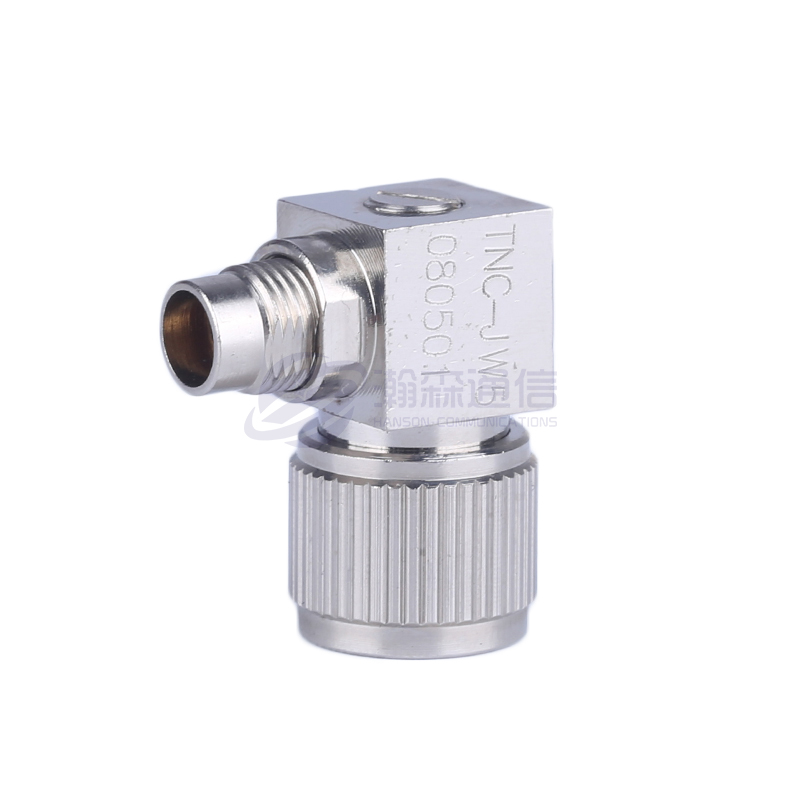
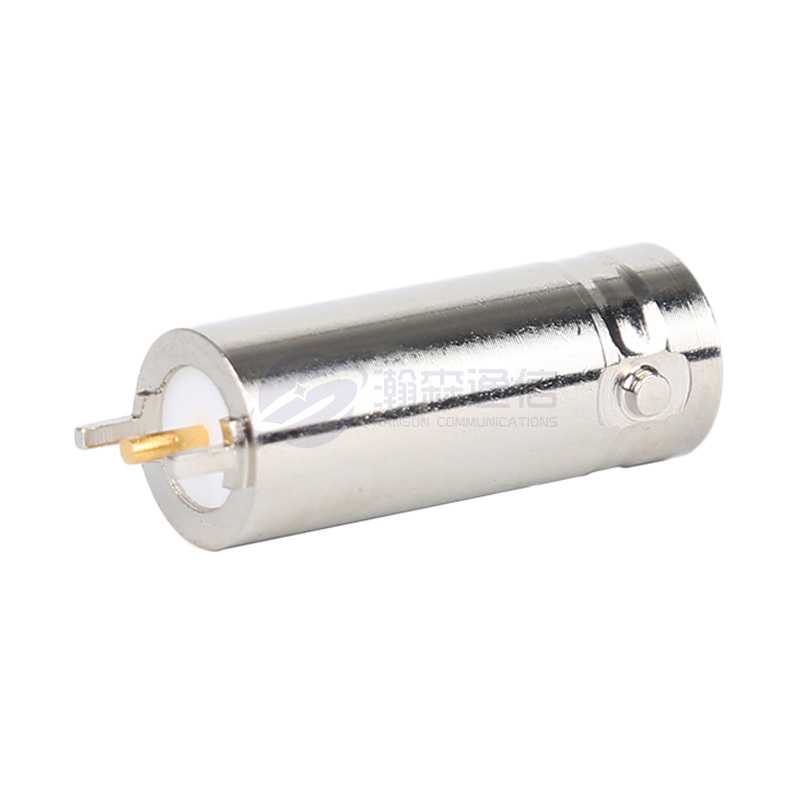
Type: Determine the type of interface you need, such as SMA, N, BNC, TNC, 3.5mm, 2.92mm (K), 2.4mm, etc.
Polarity: This is where errors are most likely to occur!
Male Connector: With a center pin/internal thread.
Female Connector: With a center hole/external thread.
Connection Combination: Specify whether you need a "male to male," "male to female," or "female to female" connection.
Connector Materials and Plating:
Housing: Typically brass, stainless steel, or nickel-plated brass. Stainless steel offers higher strength and corrosion resistance.
Center Conductor/Contact Point: Typically gold-plated beryllium copper or brass. Gold plating provides excellent conductivity, oxidation resistance, and stable contact resistance, making it the preferred choice for most applications.
Note: In applications requiring frequent mating and unplugging, plating hardness and abrasion resistance are important.
Dielectric Material: Typically polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE/Teflon) offers excellent electrical properties (low loss), high temperature resistance, and chemical stability.
Torque Requirements: Very important! Use a torque wrench to tighten the adapter.
Overtightening will damage the threads and seals, rendering the connector unusable.
Undertightening will result in poor contact, impedance discontinuities, and signal leakage.
3. Application Scenarios and Special Requirements
Depending on your specific usage environment, the following factors may also need to be considered:
Usage Environment:
Laboratory/R&D: High performance and frequency range requirements may necessitate precision adapters.
Production Testing: High durability and consistency requirements may necessitate robust industrial-grade adapters with long mating and unplugging lives.
Outdoor/Military: Waterproof, dustproof, and salt spray resistant properties are required; choose adapters with IP ratings and stainless steel construction.
Mating and Unplugging Life: The number of mating and unplugging cycles the adapter can withstand before performance degradation. Precision adapters may only last 500 cycles, while high-performance ones can last thousands. Choose according to your operating frequency.
Phase and Amplitude Consistency: In multi-channel systems (such as phased array radar), when adapters are used in pairs or groups, it is required that the phase and amplitude changes of each adapter be as consistent as possible. In this case, a high-precision adapter with "phase matching" or "performance consistency" is needed.
Request for a call today

 English
English русский
русский